SpaceX Sets New Falcon 9 Reuse Record
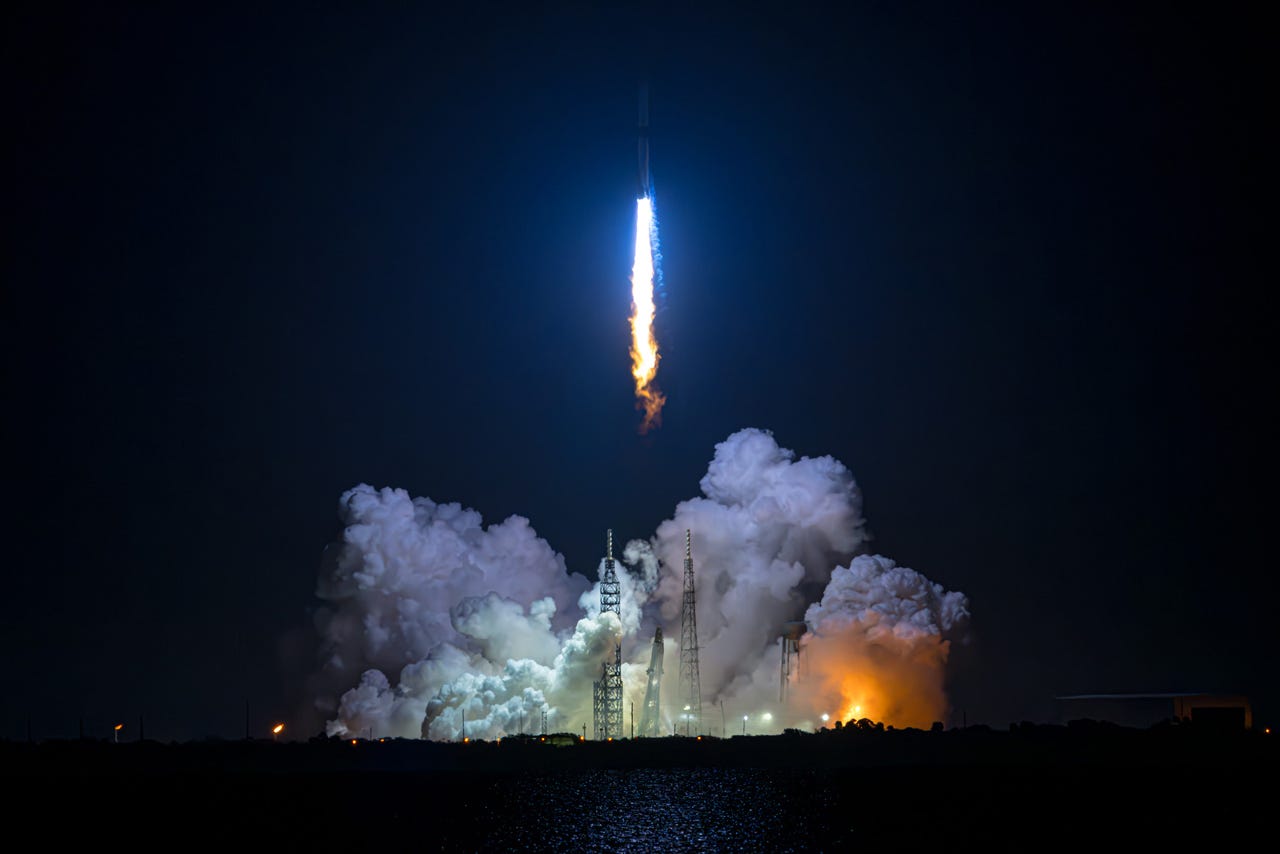
SpaceX set a new record for the reuse of its Falcon 9 booster when a first stage flew for the 26th time on Saturday. The rocket placed 21 Starlink satellites into Earth orbit after lifting off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station at 1:14 a.m. EST. The first stage touched down on an offshore drone ship.
It was the 20th launch of a Falcon 9 rocket this year, 14 of which have carried 307 Starlink satellites into orbit. SpaceX has launch 7,919 Starlink satellites into orbit on 236 Falcon 9 launches since February 2018. One booster carrying 20 satellites failed last year.
SpaceX also launched its Starship rocket on its seventh flight test in January. Starship broke up over the Caribbean after suffering a fuel leak. The Super Heavy first stage returned to its launch pad at Starbase and was captured by a set of Mechazilla chopstick arms.
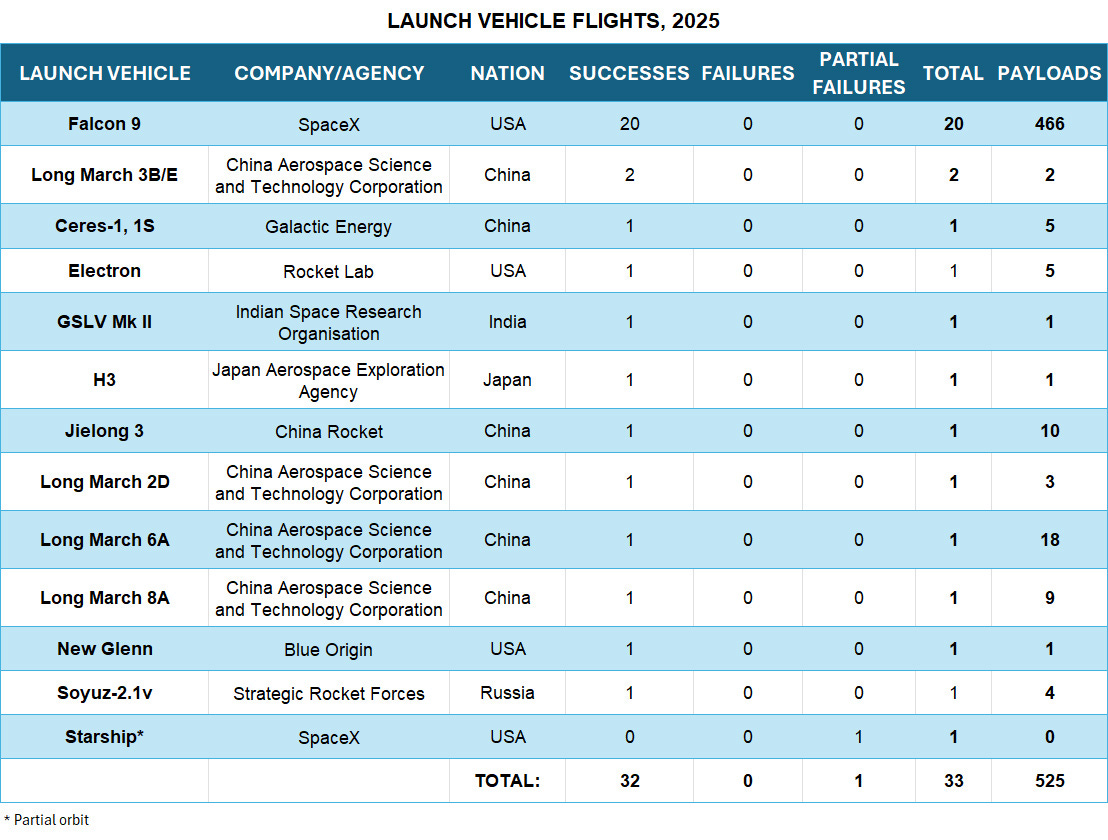
SpaceX’s 21 launches represent 63.6 percent of the 33 flights conducted through Feb. 16. The boosters have carried 466 of the 525 payloads placed in orbit in 2025.
The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) is in second place with five launches that have placed 32 payloads into orbit.
New Launchers Debut
Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket lifted off for the first time on Jan. 16 from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The booster successfully orbited Blue Ring, a platform designed to host, transport and refuel satellites. An attempt to land the booster’s first stage on the Jacklyn recovery ship failed.
New Glenn is designed to place 45,000 kg into low Earth orbit, 13,600 kg into geosynchronous transfer orbit, and 7,000 trans-lunar injection trajectory. Blue Origin is planning a second launch this spring.
On Feb. 11, an upgraded Chinese Long March 8A launched for the first time. The booster is designed to place 7,000 kg into a 700-km high sun sun-synchronous orbit compared with 5,000 kg for the standard Long March 8. The more powerful rocket features a larger, more powerful 3.5-meter diameter second stage and a larger 5.2-meter diameter fairing.
Launch Statistics
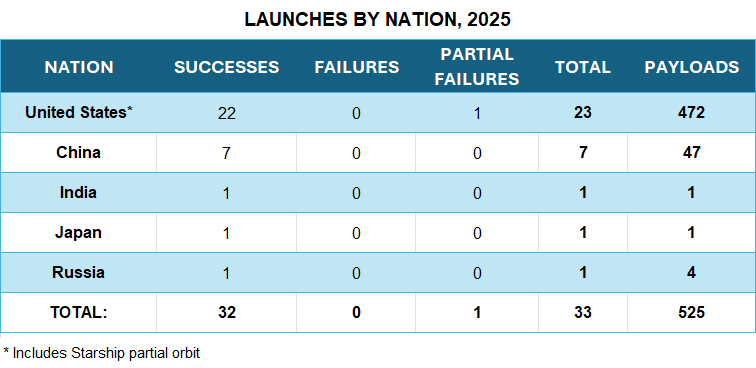
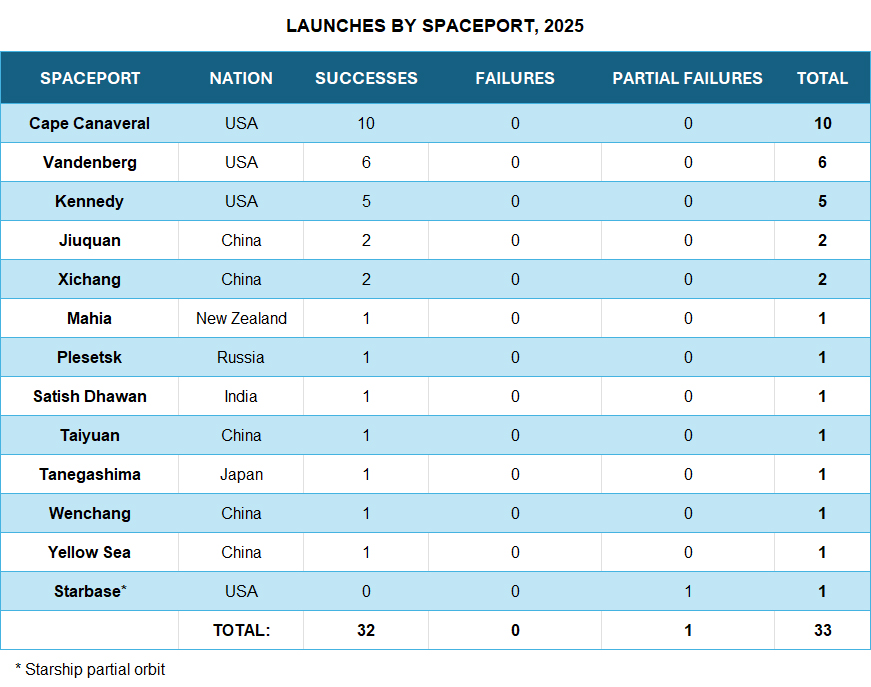
The United States leads the world with 23 launches, followed by China with seven. India, Japan and Russia have each launched one time.
There were 22 launches in January with another 11 through the first half of February. The world set a record with 263 launch attempts in 2024.
Florida remains the busiest launch site in the world with 15 launches split between Cape Canaveral and NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Vandenberg Space Force Base in California is in second place overall with six launches.
China’s seven launches have been spread across four spaceports and a ship in the Yellow Sea.
Upcoming Launches*
Flights to watch for rest of the month include the year’s second launch to the Moon on Feb. 27, a Russian Progress resupply mission to the International Space Station (ISS) on the same day, and the launch of three NASA science spacecraft on Feb. 28.
February 18 — Falcon 9 — SpaceX — Starlink — SpaceX — Communications — Cape Canaveral — USA
February 18 — Electron — Rocket Lab — BlackSky 20 — BlackSky Global — Earth observation — Mahia — New Zealand
February 19 — Falcon 9 — SpaceX — 21 Starlink — SpaceX — Communications — Vandenberg — USA
February 21 — Falcon 9 — SpaceX — Starlink — SpaceX — Communications — Cape Canaveral — USA
February 21 — Long March 3B/E — CASC — ChinaSat 9C — China Satcom — Communications — Xichang — China
February 22 — Falcon 9 — SpaceX — 21 Starshield — National Reconnaissance Office — Reconnaissance — Vandenberg — USA
February 26 — Ariane 6 — Arianespace — CSO-3 — CNES/DGA — Reconnaissance — Kourou — French Guiana
February 27 — Falcon 9 — SpaceX — Kennedy — USA
IM-2 Athena — Intuitive Machines — Lunar lander
AstroAnt — MIT — Lunar rover
MAPP LV — Lunar Outpost/Nokia — Lunar rover
Yaoki — Dymon — Lunar rover
Micro Nova Gracie — Intuitive Machines — Lunar hopper
Lunar Trailblazer — NASA/Caltech — Lunar orbiter
DOGE-1 — GEC — Lunar orbiter
Brokkr-2 Odin — AstroForge — Asteroid flyby
Chimera-1 — Epic Aerospace — Space tug
February 27 — Soyuz-2.1a — Roscosmos — Progress MS-30/91P — Roscosmos — ISS resupply — Baikonur — Kazakhstan
February 28 — Falcon 9 — SpaceX — Vandenberg — USA
SPHEREx — NASA — Near-infrared astronomy
PUNCH-NFI — NASA — Heliophysics
3 PUNCH-WFI — NASA — Heliophysics
February 28 — Ceres-1 — Galactic Energy — AIRSAT 06 (Zhongke 06), AIRSAT 07 (Zhongke 07) — Chinese Academy of Sciences — Earth observation — Jiuquan — China
* All launch dates subject to change without notice. And remember, no wagering!